Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to create a Django edit form to update a post and save the changes into the database.
This tutorial begins where creating Django flash messages tutorial left off.
We’ll create a Django Edit Form that updates a blog post and saves the changes into the database.
Create an URL pattern
First, create a URL pattern for editing a post:
from django.urls import path
from . import views
urlpatterns = [
path('', views.home, name='posts'),
path('post/create', views.create_post, name='post-create'),
path('post/edit/<int:id>/', views.edit_post, name='post-edit'),
path('about/', views.about, name='about'),
]
Code language: Python (python)The editing post URL accepts an id as an integer specified by the <int:id> pattern. For example, if you edit the post with id 1, the URL will be:
http://127.0.0.1/post/update/1/Code language: Python (python)Django will pass the id (1) to the second argument to the edit_post() function.
If you pass a value that is not an integer to the URL like this:
http://127.0.0.1/post/update/abcd/Code language: Python (python)Django will redirect to 404 because it doesn’t match any URL in the URL patterns.
Define a view function
Define the edit_post() function in the views.py file:
from django.shortcuts import render,redirect, get_object_or_404
from django.contrib import messages
from .models import Post
from .forms import PostForm
def edit_post(request, id):
post = get_object_or_404(Post, id=id)
if request.method == 'GET':
context = {'form': PostForm(instance=post), 'id': id}
return render(request,'blog/post_form.html',context)
# other functions
Code language: Python (python)How it works:
First, import get_object_or_404 function from the django.shortcuts module:
from django.shortcuts import render,redirect, get_object_or_404Code language: Python (python)The get_object_or_404() function gets an object by id or redirects to the 404 page if the id doesn’t exist.
Second, define the edit_post()HttpRequest object (request) and an id as an integer.
The edit_post()
- Get a
Postobject by id or redirect to the 404 page if the id doesn’t exist. - Create a
PostFormobject and set theinstanceargument to thepostobject. - Render the
post_form.htmltemplate.
Third, modify the post_form.html template to change the heading of the form. Currently, it shows Create Post.
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block content %}
<h2>{% if id %} Edit {% else %} New {% endif %} Post</h2>
<form method="post" novalidate>
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<input type="submit" value="Save" />
</form>
{% endblock content %}
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)If the id (post id) is available, then the form is in edit mode. Otherwise, it is in creation mode. Based on this logic, we change the heading of the form accordingly.
Fourth, modify the home.html template to include the edit link in each post:
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block content %}
<h1>My Posts</h1>
{% for post in posts %}
<h2>{{ post.title }}</h2>
<small>Published on {{ post.published_at | date:"M d, Y" }} by {{ post.author | title}}</small>
<p>{{ post.content }}</p>
<p><a href="{% url 'post-edit' post.id %}">Edit</a></p>
{% endfor %}
{% endblock content %}
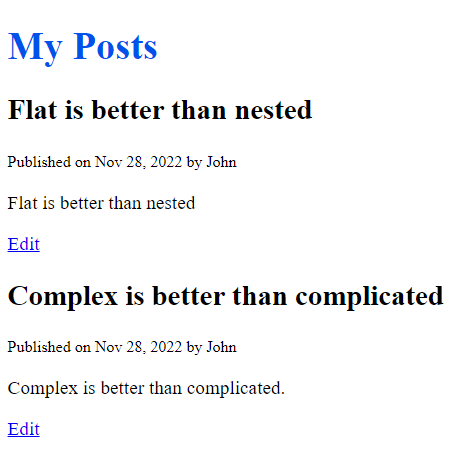
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Fifth, open the post list URL http://127.0.0.1/, you’ll see a list of posts with the edit link on each as shown in the following picture:
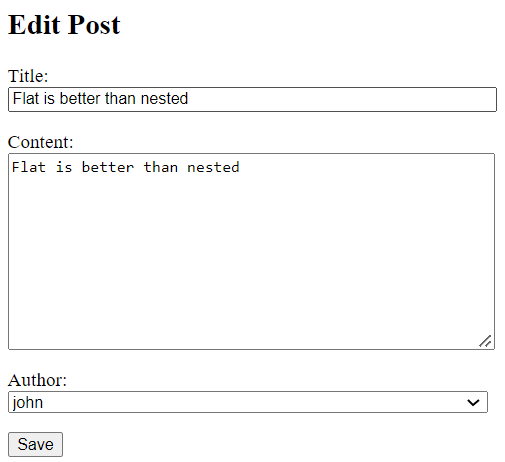
If you click the Edit link to edit a post, you’ll see a form populated with field values. For example, you can edit the post “Flat is better than nested”, you’ll see the following form:
To edit the post, you change the values and click the Save button. However, we haven’t added the code that handles the HTTP POST request yet.
Sixth, add the code that handles the HTTP POST request i.e. when the Save button is clicked:
def edit_post(request, id):
post = get_object_or_404(Post, id=id)
if request.method == 'GET':
context = {'form': PostForm(instance=post), 'id': id}
return render(request,'blog/post_form.html',context)
elif request.method == 'POST':
form = PostForm(request.POST, instance=post)
if form.is_valid():
form.save()
messages.success(request, 'The post has been updated successfully.')
return redirect('posts')
else:
messages.error(request, 'Please correct the following errors:')
return render(request,'blog/post_form.html',{'form':form})
Code language: Python (python)Update the post by appending three asterisks (***) to the title:
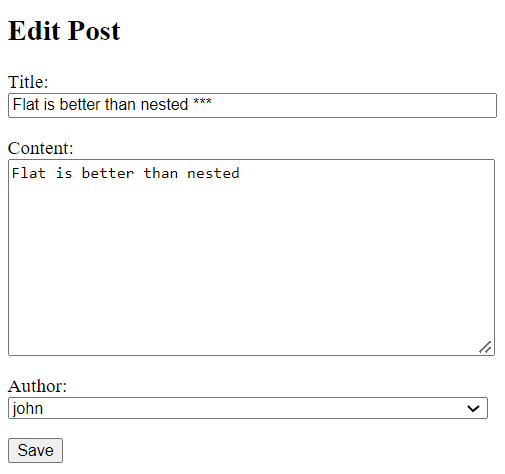
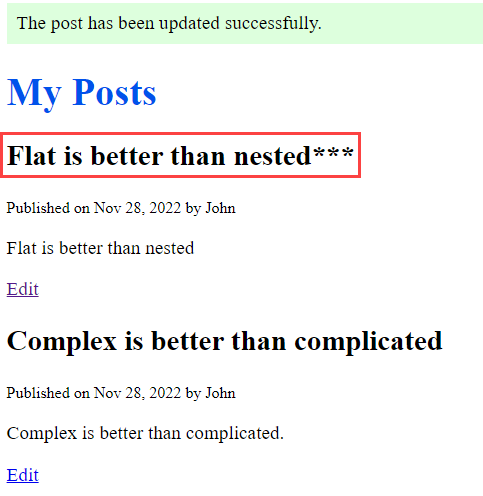
Click the Save button and you’ll see that the post will be updated:
Download the Django Project source code
Summary
- Include
<int:id>pattern in a URL to create an editing URL that accepts a model id as an integer. - Use the
get_object_or_404()function to get an object by id or redirect to the 404 page if the object doesn’t exist. - Pass a model instance to a model form to render the model fields.