Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to create multiple windows in a Tkinter application using the Tkinter Toplevel class.
Introduction to Tkinter Toplevel window
In a Tkinter application, the instance of the Tk class represents the main window.
When you destroy the main window, the application exits, and the event loop finishes.
Sometimes, you need to create additional windows. For example, you may want to create a custom dialog or a wizard form.
To do that, you can use top-level windows which are instances of the Toplevel class.
Unlike the main window, you can create as many top-level windows as you want.
To show a Toplevel window from the main window, you follow these steps:
First, create an instance of the Toplevel class and set its parent to the root window:
window = tk.Toplevel(root)Code language: Python (python)The moment you create the Toplevel window, it’ll display on the screen.
Second, add widgets to the Toplevel window like you do with the frames and main window.
Third, call the grab_set() method of the Toplevel window instance to allow it to receive events and prevent users from interacting with the main window:
window.grab_set()Code language: Python (python)A simple Tkinter Toplevel Window example
The following program displays a window that has one button:
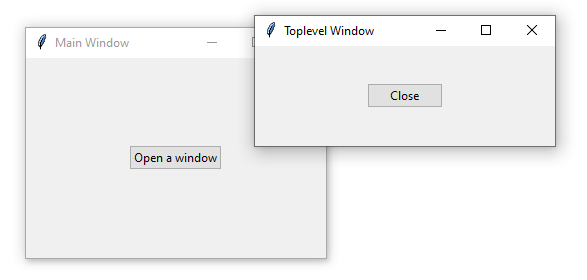
When you click the button, it’ll open a Toplevel window. The Toplevel window also consists of a button.
If you click or press the Close button, the Toplevel window closes.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
class Window(tk.Toplevel):
def __init__(self, parent):
super().__init__(parent)
self.geometry('300x100')
self.title('Toplevel Window')
ttk.Button(self,
text='Close',
command=self.destroy).pack(expand=True)
class App(tk.Tk):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.geometry('300x200')
self.title('Main Window')
# place a button on the root window
ttk.Button(self,
text='Open a window',
command=self.open_window).pack(expand=True)
def open_window(self):
window = Window(self)
window.grab_set()
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = App()
app.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)How it works.
First, define a class Window that inherits from the Toplevel window. The Window will be closed once the Close button is clicked.
Second, assign the command of the Open a window button to the open_window() method in the App class
Third, in the open_window() method, create a new instance of the Window and call the grab_set() method so that it can receive events. The grab_set() method also prevents users from interacting with the main window.
Summary
- Show additional windows by creating instances of the
Toplevelclass. - Use
grab_set()method so that theToplevelwindow can receive events and prevents users from interacting with the main window.