Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use PyQt QGridLayout to arrange widgets in uniform rows and columns.
Introduction to the PyQt QGridLayout
The QGridLayout allows you to place widgets in uniform rows and columns of a grid. For example, the following picture shows a grid that consists of four columns and three rows:
Rows and columns are zero-based indexing. It means that the first row has an index of zero, the second row has an index of one, and so on. Similarly, the first column has an index of zero, the second column has an index of one, etc.
The intersection between a row and a column is called a cell. A cell is a space where you can place a widget.
Rows and columns can span. For example, the following picture illustrates that the second column of the first row spans two columns and the second row of the second column spans two rows:
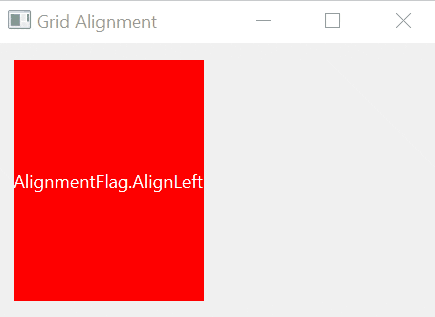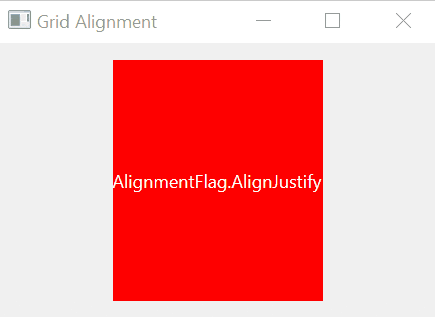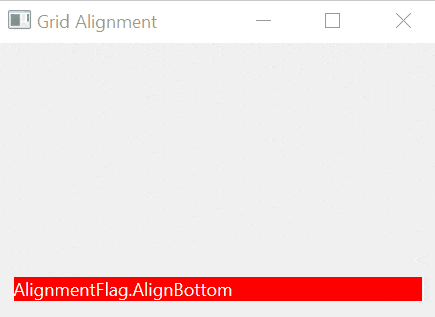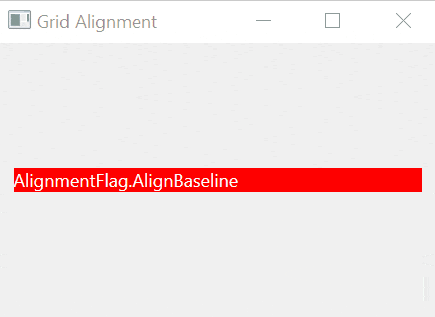
If a widget takes less space than the containing cell, you can align it within the cell using one of the following alignment options:
| Alignment Flag | Meaning |
|---|---|
AlignAbsolute | If the direction is left to right, the AlignLeft means align with the right edge. However, if you want AlignLeft to be always aligned with the left edge, you can combine the AlignLeft with the AlignAbsolute option. |
AlignBaseline | Align the widget with the baseline. |
AlignBottom | Align the widget with the bottom edge. |
AlignCenter | Centers the widget in both dimensions. |
AlignHCenter | Centers the widget horizontally in the available space. |
AlignHorizontal_Mask | |
AlignJustify | Justifies the text in the available space. |
AlignLeft | Align the widget with the left edge. |
AlignRight | Align the widget with the right edge. |
AlignTop | Align the widget with the top edge. |
AlignVCenter | Centers the widget vertically in the available space. |
AlignVertical_Mask | |
Using a QGridLayout
To use the QGridLayout, you follow these steps:
First, create a QGridLayout object:
layout = QGridLayout()Code language: Python (python)Second, set the parent widget layout:
parent.setLayout(layout)Code language: Python (python)Third, place the child widgets on the grid layout:
layout.addWidget(widget, row, column, rowSpan, columnSpan, alignment)Code language: Python (python)In this syntax:
widgetis a child widget that you want to place on the grid.rowis a row index that starts from 0.columnis a column index that starts from 0.rowSpanis the number of rows that you want to span.columnSpanis the number of columns that you want to span.alignmentspecifies the alignment of the widget within the cell.
To get the alignment value, you import Qt from PyQt6.QtCore:
from PyQt6.QtCore import QtCode language: Python (python)and use one of the values of the Qt.AlignmentFlag enum, for example:
Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignRightCode language: Python (python)PyQt QGridLayout example
The following example shows how to create a login form using the QGridLayout:
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QPushButton, QLineEdit, QLabel, QGridLayout
from PyQt6.QtCore import Qt
class MainWindow(QWidget):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.setWindowTitle('Login Form')
# set the grid layout
layout = QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# username
layout.addWidget(QLabel('Username:'), 0, 0)
layout.addWidget(QLineEdit(), 0, 1)
# password
layout.addWidget(QLabel('Password:'), 1, 0)
layout.addWidget(QLineEdit(echoMode=QLineEdit.EchoMode.Password), 1, 1)
# buttons
layout.addWidget(QPushButton('Log in'), 2, 0,
alignment=Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignRight)
layout.addWidget(QPushButton('Close'), 2, 1,
alignment=Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignRight)
# show the window
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
sys.exit(app.exec())
Code language: Python (python)Output:
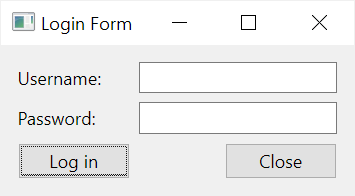
How it works.
First, create a QGridLayout object:
layout = QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)Code language: Python (python)Second, place a QLabel on the cell (0,0) and QLineEdit on the cell (0,1) for creating the username field:
layout.addWidget(QLabel('Username:'), 0, 0)
layout.addWidget(QLineEdit(), 0, 1)Code language: Python (python)Third, place a QLabel on the cell (1,0) and QLineEdit on the cell (1,1) for creating the password field:
layout.addWidget(QLabel('Password:'), 1, 0)
layout.addWidget(QLineEdit(echoMode=QLineEdit.EchoMode.Password), 1, 1)Code language: Python (python)Finally, place a login button on the cell (2,0) and align it to the left edge. Also, place the close button on the cell (2,1) and align it to the right edge.
# buttons
layout.addWidget(QPushButton('Log in'), 2, 0,
alignment=Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignRight)
layout.addWidget(QPushButton('Close'), 2, 1,
alignment=Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignRight)Code language: Python (python)Summary
- Use PyQt
QGridLayoutto arrange widgets in rows and columns.