Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the Tkinter Listbox widget to display a list of items.
Introduction to the Tkinter Listbox #
A Listbox widget displays a list of single-line text items. A Listbox allows you to browse through the items and select one or multiple items at once.
To create a Listbox widget, you follow these steps:
First, import the tkinter as the tk module:
import tkinter as tkCode language: Python (python)Second, create a listbox widget using Listbox constructor:
tk.Listbox(master=None, cnf={}, **kw)Code language: Python (python)In this syntax:
master: The window or frame where you want to place theListboxwidget.cnf: a dictionary that specifies the configurations of theListboxwidget.**kwone or more keyword arguments that specify additional configuration for the widget.
Adding List Items #
To add items to a Listbox widget:
First, create a Variable object and initialize its value to the list of items:
list_items = tk.Variable(value=items)Code language: Python (python)Second, assign this Variable object to the listvariable option of the Listbox widget:
tk.Listbox(listvariable=list_items)Code language: Python (python)You can modify the list_items variable to manipulate list items such as adding, changing, and removing.
The following program create a Listbox widget:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
# create the main window
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry('400x180')
root.title('Listbox')
# create a variabe object
languages = ('Java', 'C', 'C++', 'C#', 'Python',
'Go', 'JavaScript', 'PHP', 'Swift')
list_variable = tk.Variable(value=languages)
# label
label = ttk.Label(
root,
text='Select your favorite programming languages:'
)
label.pack(padx=10, pady=0, side=tk.TOP, fill=tk.X)
listbox = tk.Listbox(
root,
listvariable=list_variable,
height=6,
)
listbox.pack(padx=10, pady=10, expand=True, fill=tk.BOTH, side=tk.LEFT)
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Output:
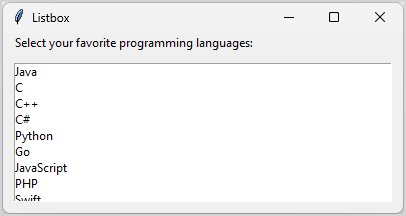
How it works:
First, create a Variable object and initialize its value to a tuple:
# create a variabe object
languages = ('Java', 'C', 'C++', 'C#', 'Python',
'Go', 'JavaScript', 'PHP', 'Swift')
list_variable = tk.Variable(value=languages)Code language: Python (python)Second, create a Listbox widget and assign the list_variable to the listvariable option:
listbox = tk.Listbox(
root,
listvariable=list_variable,
height=6
)Code language: Python (python)Third, pack the Listboxwidget on the main window:
listbox.pack(padx=10, pady=10, expand=True, fill=tk.BOTH, side=tk.LEFT)Code language: Python (python)Setting a Selection Mode #
The selectmode option determines how many items you can select and how the mouse drags will affect the items:
tk.BROWSE– allows a single selection. If you select an item and drag it to a different line, the selection will follow the mouse. This is the default.tk.EXTENDED– select any adjacent group of items at once by clicking the first item and dragging to the last line.tk.SINGLE– allow you to select one line and you cannot drag the mouse.tk.MULTIPLE– select any number of lines at once. Clicking on any line toggles whether it is selected or not.
The following program sets the selection mode of the Listbox widget to tk.MULTIPLE:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
# create the main window
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry('400x180')
root.title('Listbox')
# create a variabe object
languages = ('Java', 'C', 'C++', 'C#', 'Python',
'Go', 'JavaScript', 'PHP', 'Swift')
list_variable = tk.Variable(value=languages)
# label
label = ttk.Label(
root,
text='Select your favorite programming languages:'
)
label.pack(padx=10, pady=0, side=tk.TOP, fill=tk.X)
listbox = tk.Listbox(
root,
listvariable=list_variable,
height=6,
selectmode=tk.MULTIPLE,
)
listbox.pack(padx=10, pady=10, expand=True, fill=tk.BOTH, side=tk.LEFT)
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)In this example, we set the select mode to tk.MULTIPLE:
listbox = tk.Listbox(
root,
listvariable=list_variable,
height=6,
selectmode=tk.MULTIPLE,
)Code language: Python (python)Binding the selected event #
If you want to execute a function automatically when users select a list item, you can bind that function to the <<ListboxSelect>> event:
listbox.bind('<<ListboxSelect>>', callback)Code language: Python (python)For example:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter.messagebox import showinfo
from tkinter import ttk
# create the main window
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry('400x180')
root.title('Listbox')
# create a variabe object
languages = ('Java', 'C', 'C++', 'C#', 'Python',
'Go', 'JavaScript', 'PHP', 'Swift')
list_variable = tk.Variable(value=languages)
# label
label = ttk.Label(
root,
text='Select your favorite programming languages:'
)
label.pack(padx=10, pady=0, side=tk.TOP, fill=tk.X)
listbox = tk.Listbox(
root,
listvariable=list_variable,
height=6,
selectmode=tk.MULTIPLE,
)
listbox.pack(padx=10, pady=10, expand=True, fill=tk.BOTH, side=tk.LEFT)
def handle_item_select(event):
selected_indices = listbox.curselection()
selected_languages = ",".join([listbox.get(i) for i in selected_indices])
showinfo(
title='Information',
message=f'You selected: {selected_languages}'
)
listbox.bind('<<ListboxSelect>>', handle_item_select)
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Output:
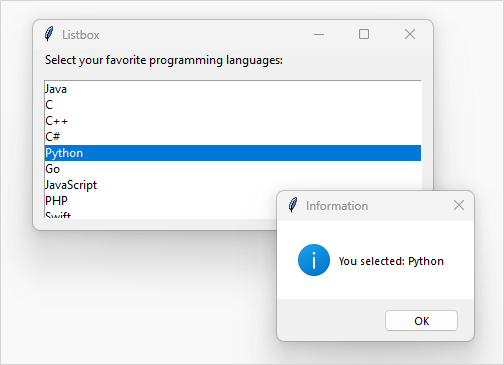
First, define a function handle_item_select to display selected items:
def handle_item_select(event):
selected_indices = listbox.curselection()
selected_languages = ",".join([listbox.get(i) for i in selected_indices])
showinfo(
title='Information',
message=f'You selected: {selected_languages}'
)Code language: Python (python)In the function:
- Get the currently selected list items using the
curselection()method of the listbox instance. - Concatenate selected items into a single string.
- Display the result string in a message box.
Second, bind the handle_item_select function to the item select event:
listbox.bind('<<ListboxSelect>>', handle_item_select)Code language: Python (python)Adding a scrollbar to the Listbox #
The following program illustrates how to add a scrollbar to a Listbox:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter.messagebox import showinfo
from tkinter import ttk
# create the main window
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry('400x180')
root.title('Listbox')
# create a variabe object
languages = ('Java', 'C', 'C++', 'C#', 'Python',
'Go', 'JavaScript', 'PHP', 'Swift')
list_variable = tk.Variable(value=languages)
# label
label = ttk.Label(
root,
text='Select your favorite programming languages:'
)
label.pack(padx=10, pady=0, side=tk.TOP, fill=tk.X)
listbox = tk.Listbox(
root,
listvariable=list_variable,
height=6,
selectmode=tk.MULTIPLE,
)
listbox.pack(padx=10, pady=10, expand=True, fill=tk.BOTH, side=tk.LEFT)
def handle_item_select(event):
selected_indices = listbox.curselection()
selected_languages = ",".join([listbox.get(i) for i in selected_indices])
showinfo(
title='Information',
message=f'You selected: {selected_languages}'
)
listbox.bind('<<ListboxSelect>>', handle_item_select)
# link a scrollbar to a list
v_scrollbar = ttk.Scrollbar(
root,
orient=tk.VERTICAL,
command=listbox.yview
)
listbox['yscrollcommand'] = v_scrollbar.set
v_scrollbar.pack(pady=10, side=tk.RIGHT, fill=tk.Y)
root.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Output:
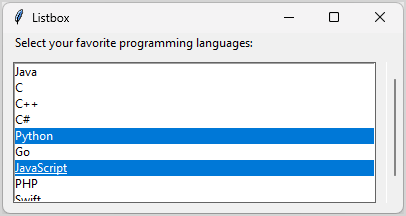
First, create a Scrollbar widget and link it to the Listbox widget:
v_scrollbar = ttk.Scrollbar(
root,
orient=tk.VERTICAL,
command=listbox.yview
)Code language: Python (python)Second, allow the Listbox to communicate its scroll state to the Scrollbar:
listbox['yscrollcommand'] = v_scrollbar.setCode language: Python (python)For more information on how to link a scrollbar to a scrollable widget, check out the scrollbar widget tutorial.
Summary #
- Use the
tk.Listbox(container, height, listvariable)to create a Listbox widget; alistvariableshould be atk.StringVar(value=items). - Bind a callback function to the
'<<ListboxSelect>>'event to execute the function when one or more list items are selected.