Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn about the Python set intersection and how to use it to intersect two or more sets.
TL;DR
In Python, you can use the set intersection() method or set intersection operator (&) to intersect two or more sets:
new_set = set1.intersection(set2, set3)
new_set = set1 & set2 & set3The intersection() method and & operator have the same performance.
Introduction to Python set intersection
When intersecting two or more sets, you’ll get a new set consisting of elements that exist in all sets.
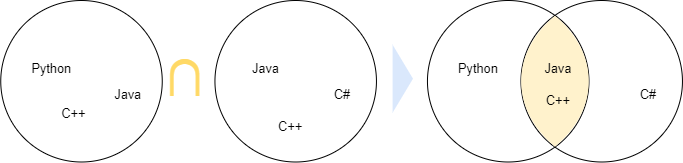
Suppose that you have two following sets s1 and s2:
s1 = {'Python', 'Java','C++'}
s2 = {'C#', 'Java', 'C++' }Code language: JavaScript (javascript)The intersection of these two sets returns a new set that contains two elements 'Java' and 'C++':
s = {'Java', 'C++'}Code language: JavaScript (javascript)… because they’re the only elements that exist in both sets.
The following Venn diagram illustrates the intersection of two sets s1 and s2:
The set intersection has many useful applications. For example, you can use set intersections to find the common favorites of two friends on a social networking application or to search for common skills of two or more employees on an HR application.
In Python, you can intersect two or more sets using the set intersection() method or set intersection operator (&).
1) Using Python set intersection() method to intersect two or more sets
This example shows how to use the set intersection() method to intersect two or more sets:
new_set = set1.intersection(set2, set3, ...)
The following shows how to use the intersection() method to intersect the sets s1 and s2:
s1 = {'Python', 'Java', 'C++'}
s2 = {'C#', 'Java', 'C++'}
s = s1.intersection(s2)
print(s)
Code language: PHP (php)Output:
{'C++', 'Java'}
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)2) Using Python set intersection (&) operator to intersect two or more sets
Python provides you with the set intersection operator (&) that allows you to intersect two or more sets:
new_set = s1 & s2 & s3 & ...The following example uses the set intersection operator (&) to intersect the sets s1 and s2:
s1 = {'Python', 'Java', 'C++'}
s2 = {'C#', 'Java', 'C++'}
s = s1 & s2
print(s)Code language: PHP (php)Output:
new_set = s1 & s2 & s3 & ...Set intersection() method vs set intersection operator (&)
The set intersection operator only allows sets, while the set intersection() method can accept any iterables, like strings, lists, and dictionaries.
If you pass iterables to the intersection() method, it’ll convert the iterables to set before intersecting them.
However, the set intersection operator (&) will raise an error if you use it with iterables.
The following example uses the intersection() method to intersect a set with a list:
numbers = {1, 2, 3}
scores = [2, 3, 4]
numbers = numbers.intersection(scores)
print(numbers)Code language: PHP (php)Output:
{2, 3}If you use the set intersection operator (&) instead, you’ll get an error:
numbers = {1, 2, 3}
scores = [2, 3, 4]
numbers = numbers & scores
print(numbers)Code language: PHP (php)Output:
TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for &: 'set' and 'list'Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Summary
- The intersection of two or more sets returns elements that exist in all sets.
- Use the
intersection()method or set intersection operator (&) to intersect two or more sets.